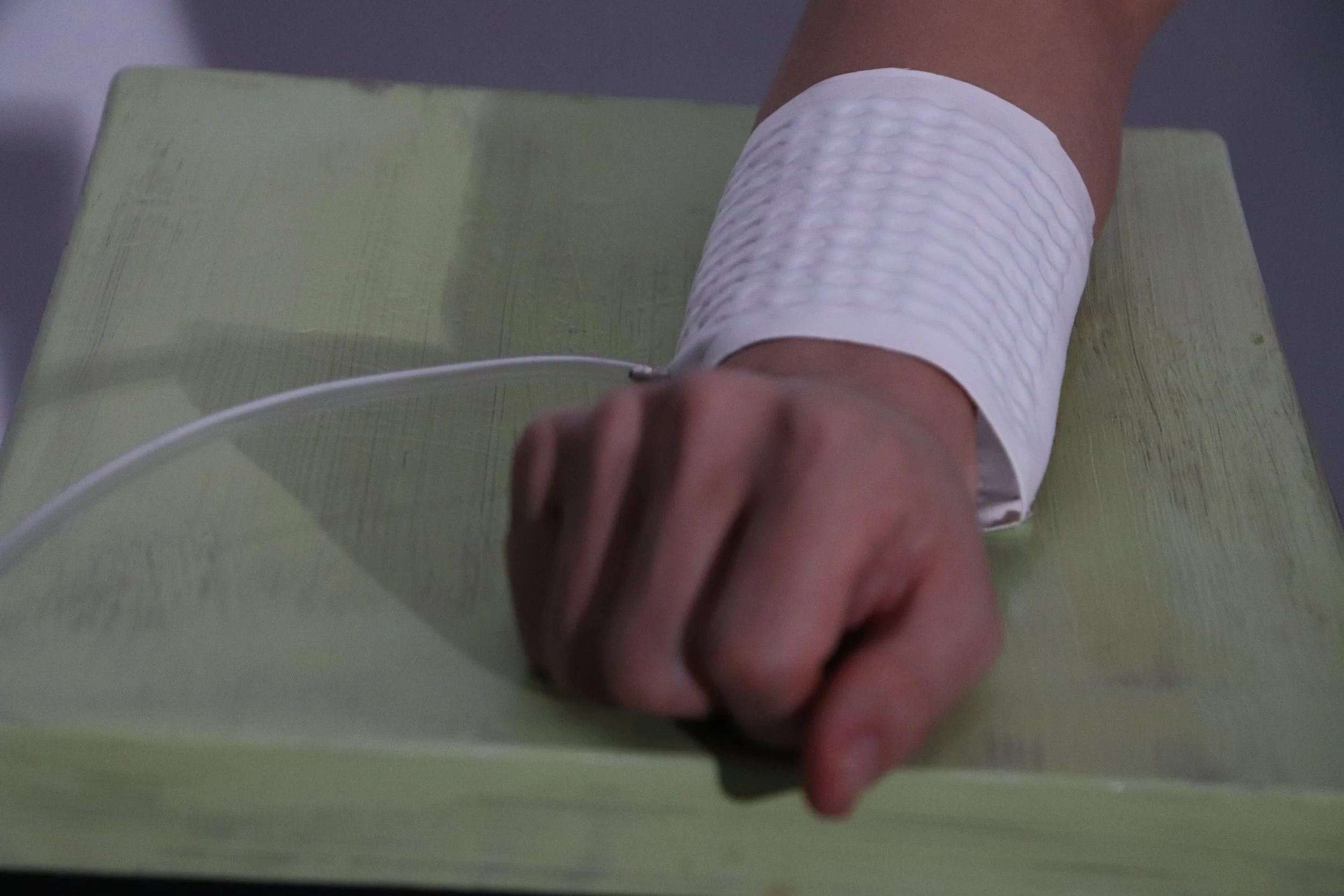
Popping Skin
"Popping Skin" redefines the music consumption experience. By converting sound into tactile vibrations, this innovative project establishes a seamless connection between auditory and tactile senses.
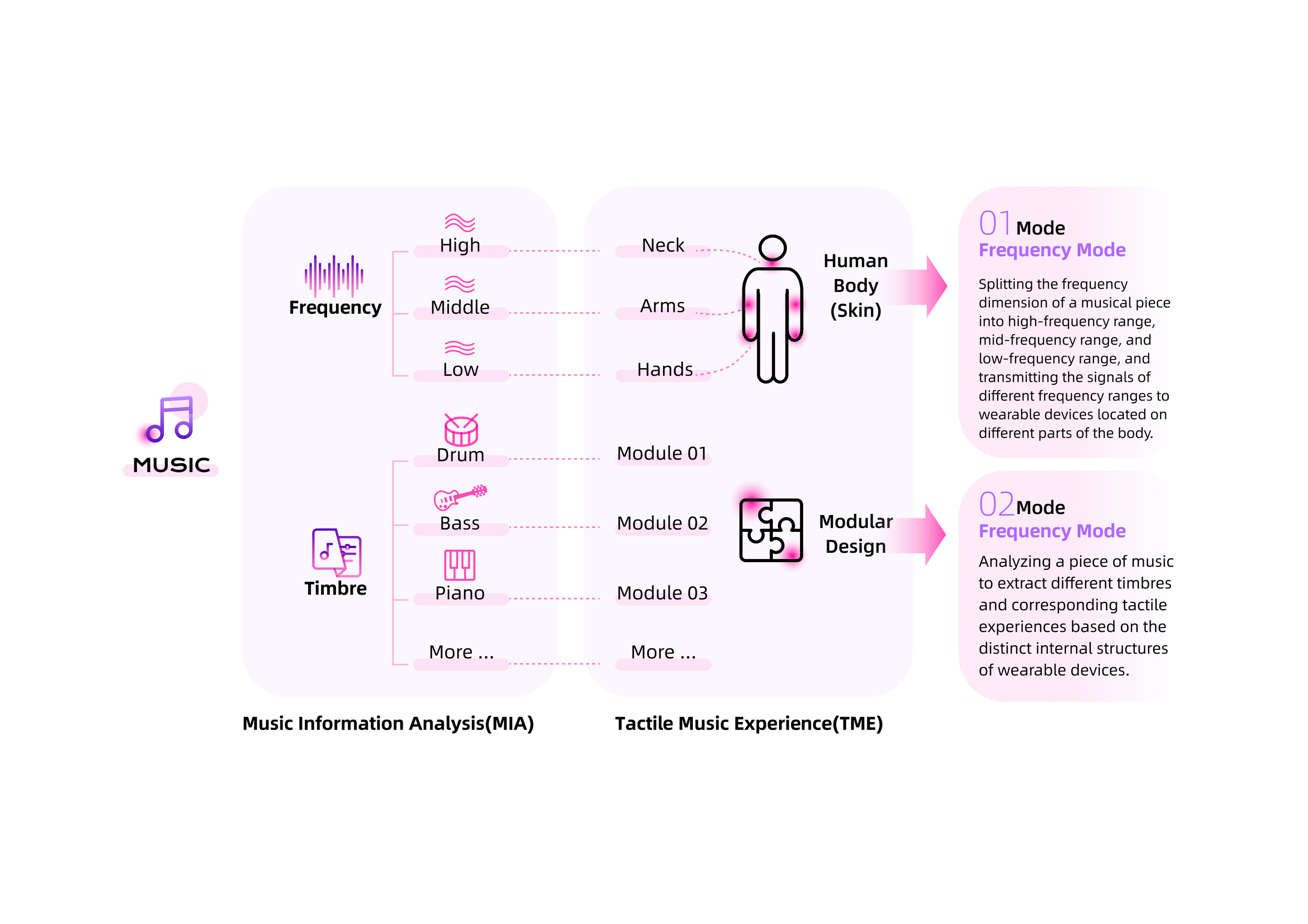
One mode involves mapping different frequency ranges of music to specific areas of the body, while another mode associates various tones with distinct tactile sensations.
As a novel music interface, "Popping Skin" not only enhances our sensory experience and emotional connection while listening to music but also serves as a means for the hearing-impaired to perceive and enjoy music.
Personal Project
Year: 2022
Location: Shanghai, China
Observation and Research
Phone Vibrating with a Low-Frequency Sound
When a mobile phone vibrates during an incoming call, it is accompanied by a noticeably low-frequency sound. If it happens to be in your pocket or hand, the sensation will be very strong.
Powerful Sound Wave in the Livehouse
At a livehouse venue, we can experience the intense sensory and emotional impact that music brings. This includes a kind of sound wave, or vibration, that our bodies feel when music is amplified by high-powered sound systems.
The Hearing Impared Individuals
The hearing impairment among the deaf community is highly diverse. Some individuals may perceive low-frequency sounds, such as drums and bass, while struggling to pick up relatively high-frequency elements like human voices and guitars. In some cases, hearing aids and cochlear implants can serve as solutions. However, even for profoundly deaf individuals, they can engage with music by capturing vibrations through the skin, dancing to the beats they feel in their bodies.
Sound
Sound is the phenomenon of waves generated by vibrations, transmitted through a medium (gas, solid, liquid), and perceptible by the auditory organs of humans or animals.
Auditory-Tactile Synesthesia
Tactile Sense
The sense of touch is one of the fundamental sensations of the skin. The skin surface is covered with numerous touch receptors, varying in size, with some having a diameter of up to 0.5mm.
Hearing sounds leads to specific sensations in parts of the body. It’s as if you’re being touched, but nothing is touching you. For example, hearing heavy metal music might feel like pins and needles on your legs.
It can be triggered by both musical and non-musical sounds, and it varies from person to person. In many cases the sound of each musical instrument is felt in a different part of the body or has its own specific tactile sensation, which is always consistent, so the inducer in this case is timbre.
Alternatively, it may be specific to each song or musical genre. Although apparently much less common, auditory-tactile synesthesia can also be prompted by the different musical pitches (frequencies), keys or chords.
Interaction System
Interaction Testing
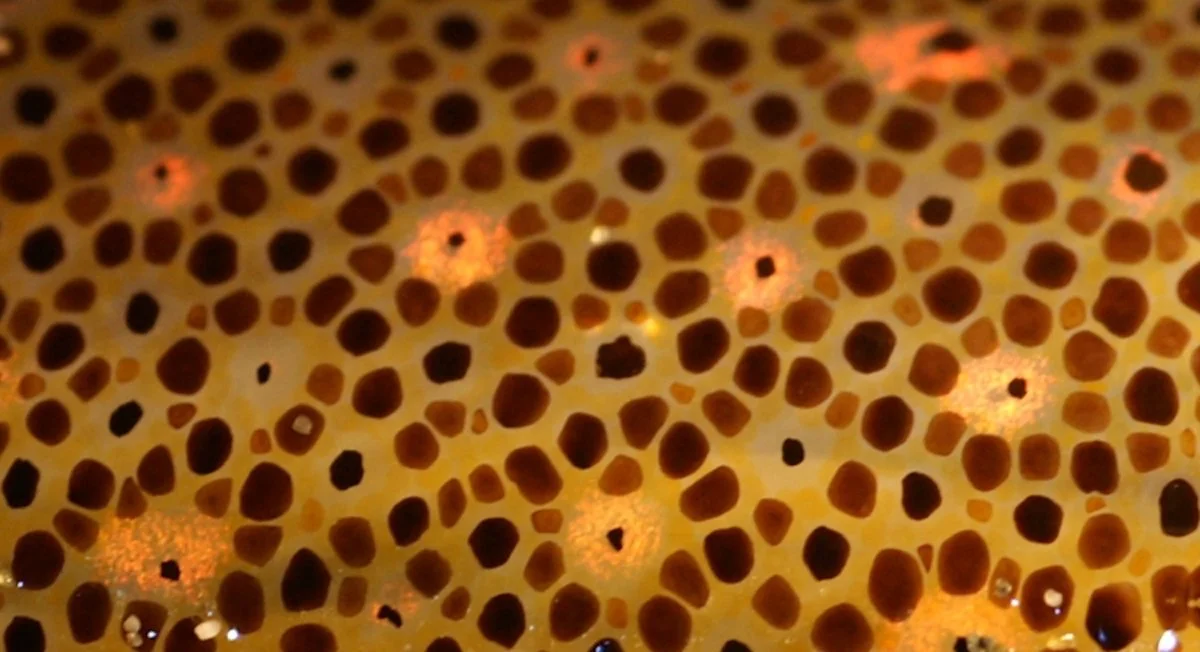
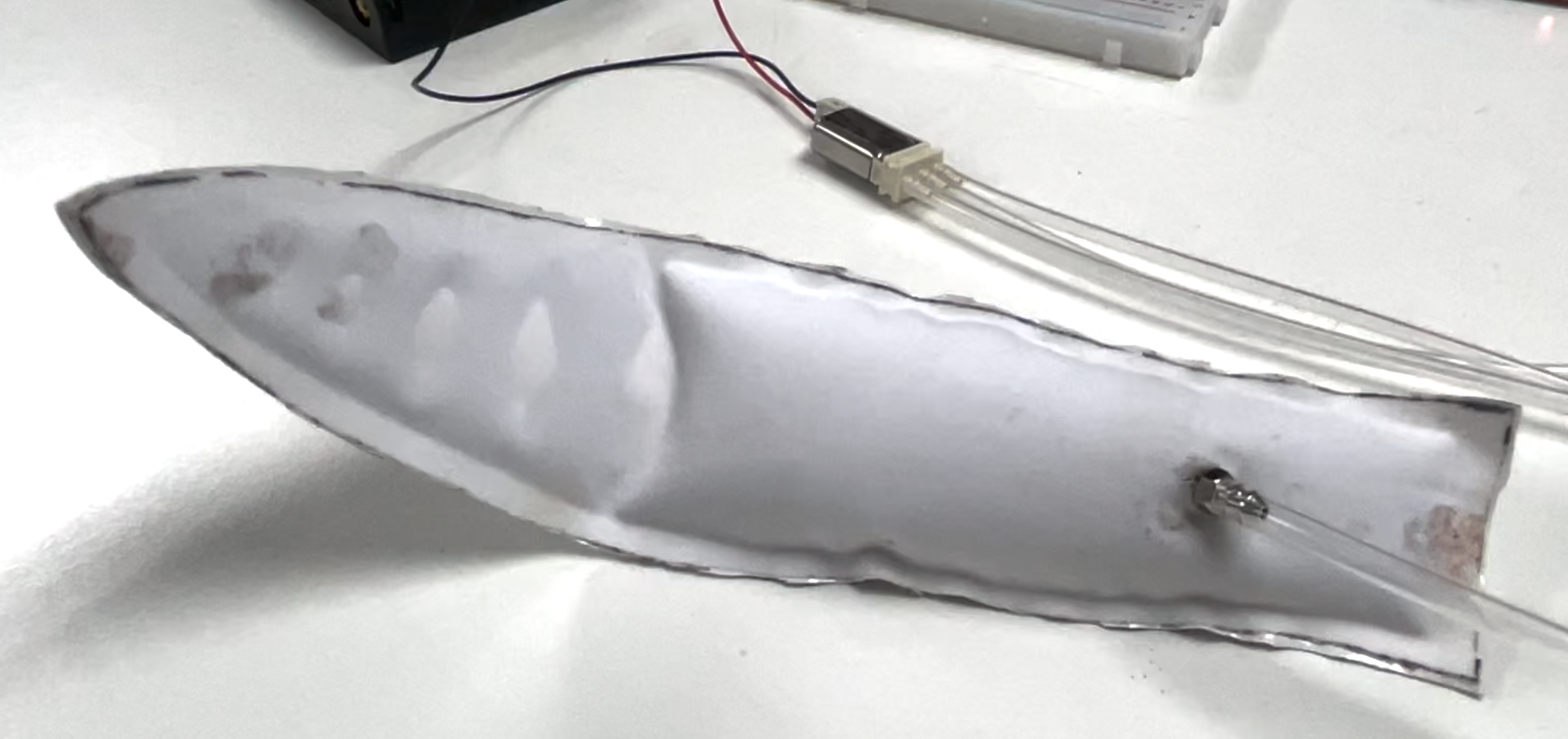
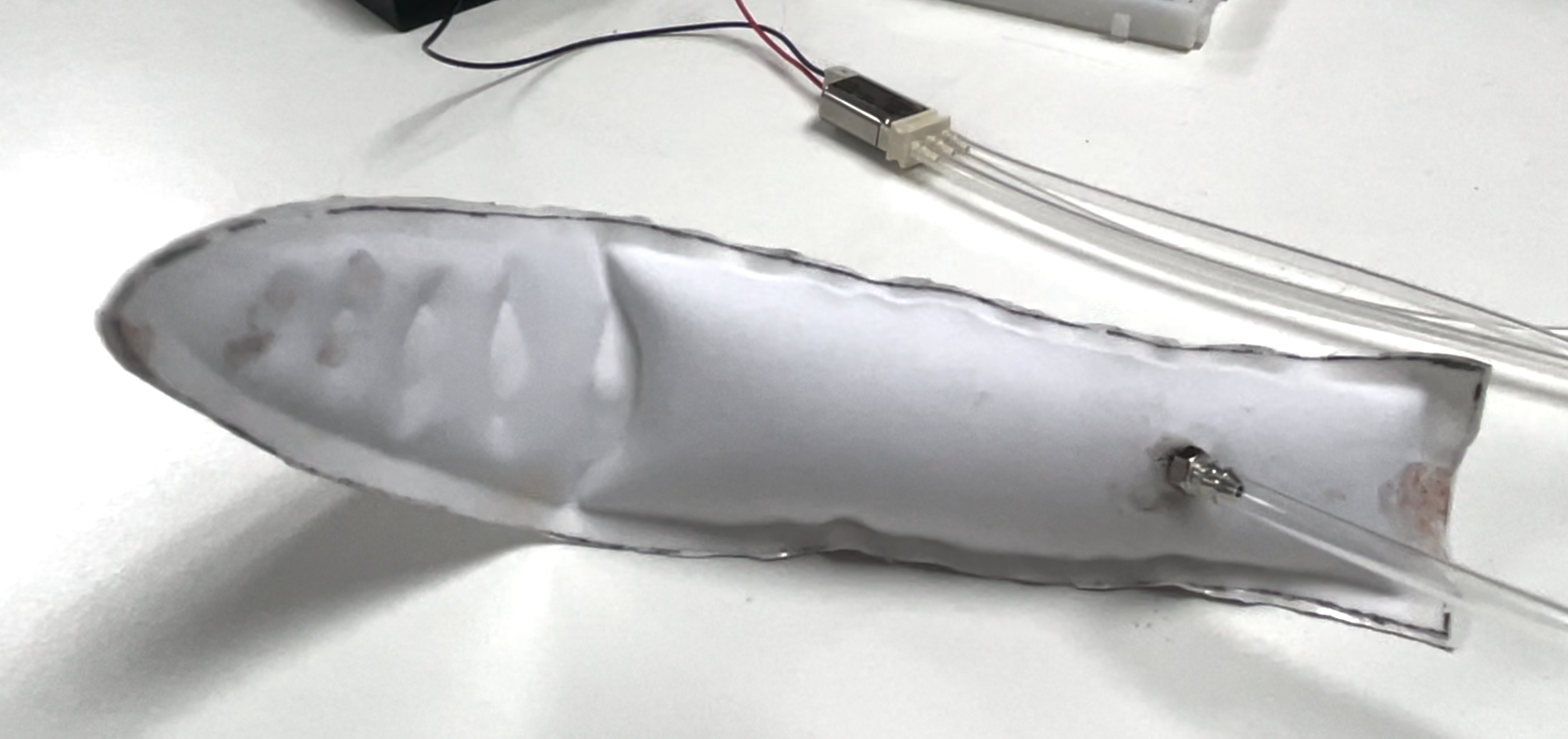
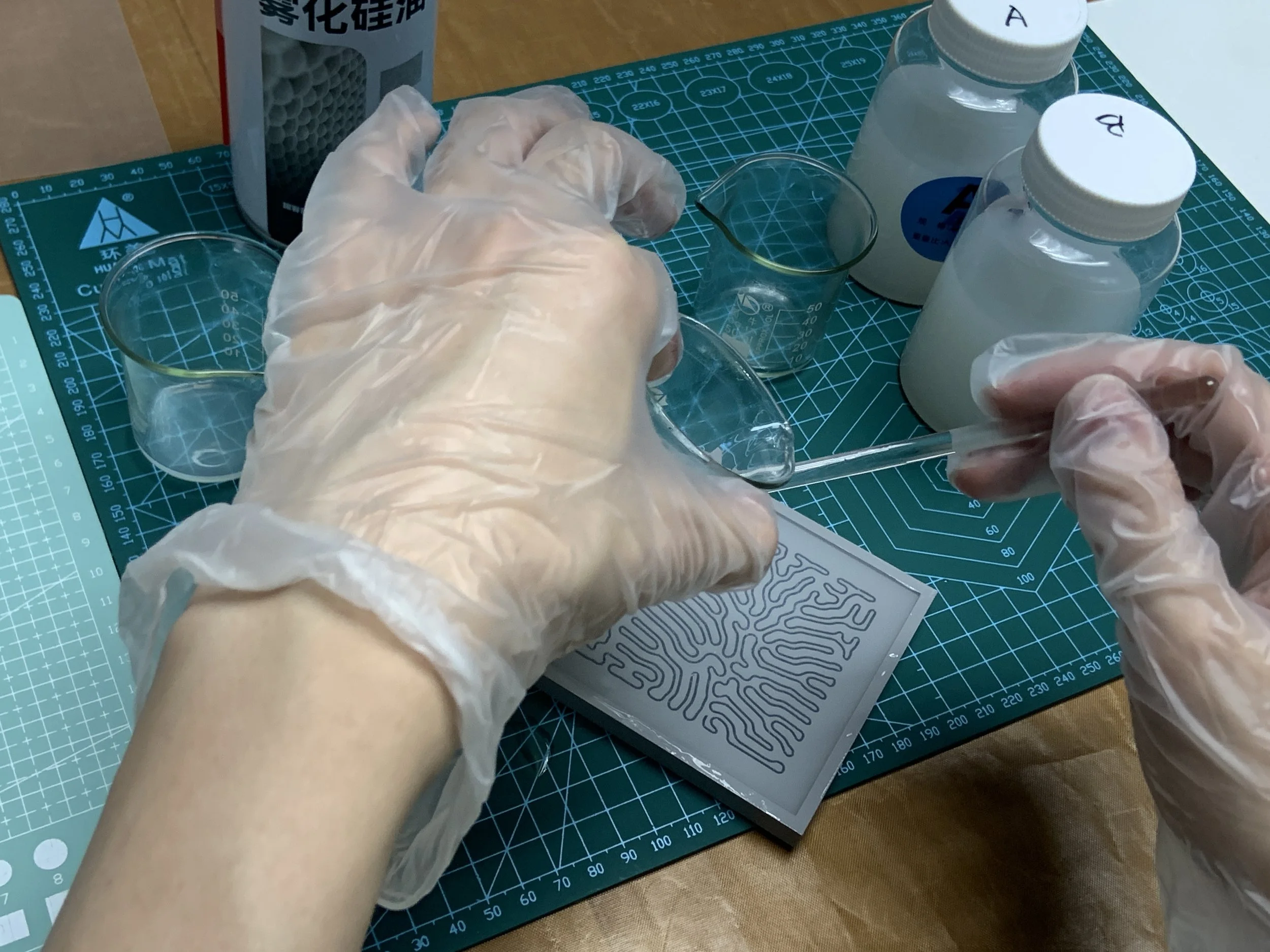
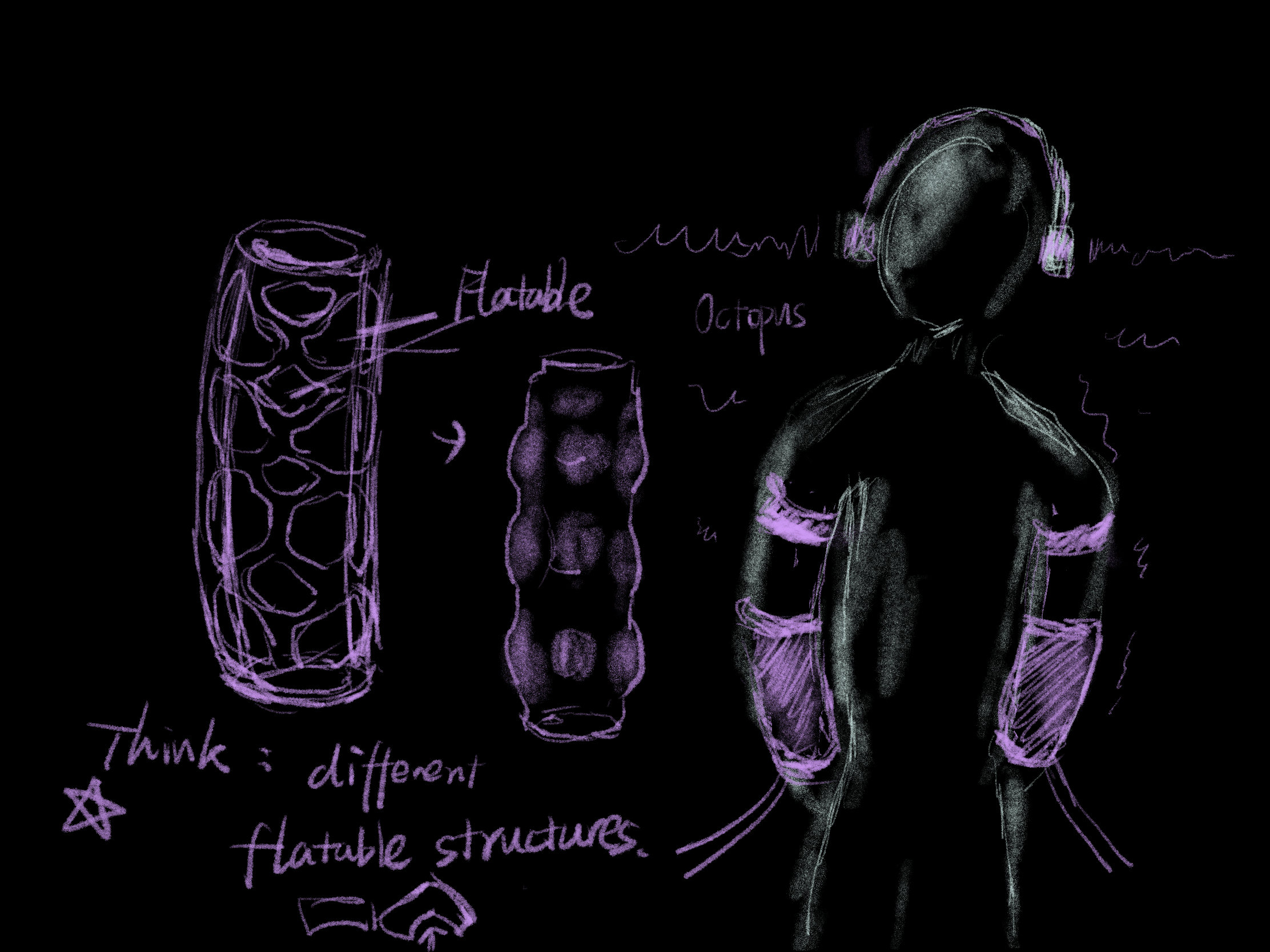
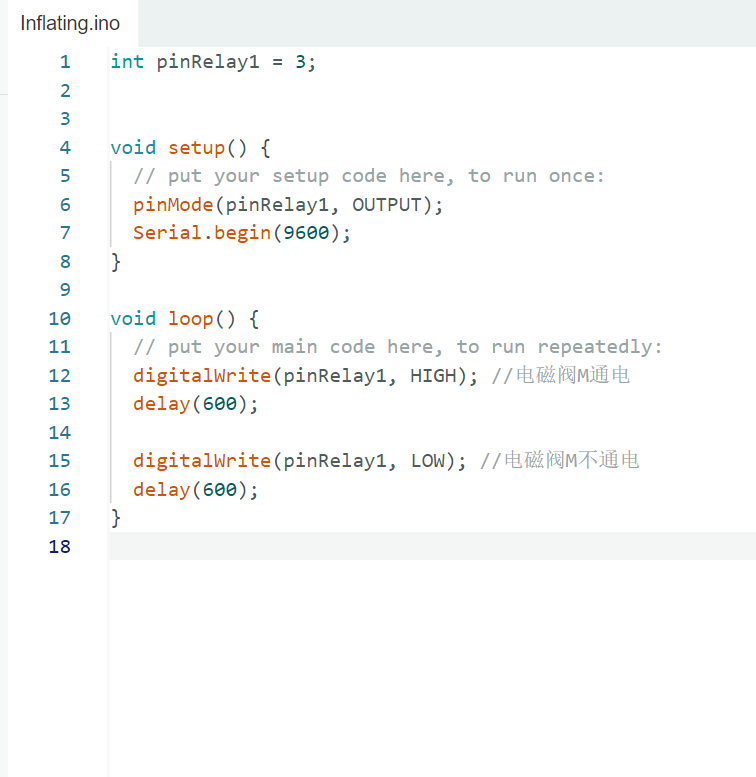
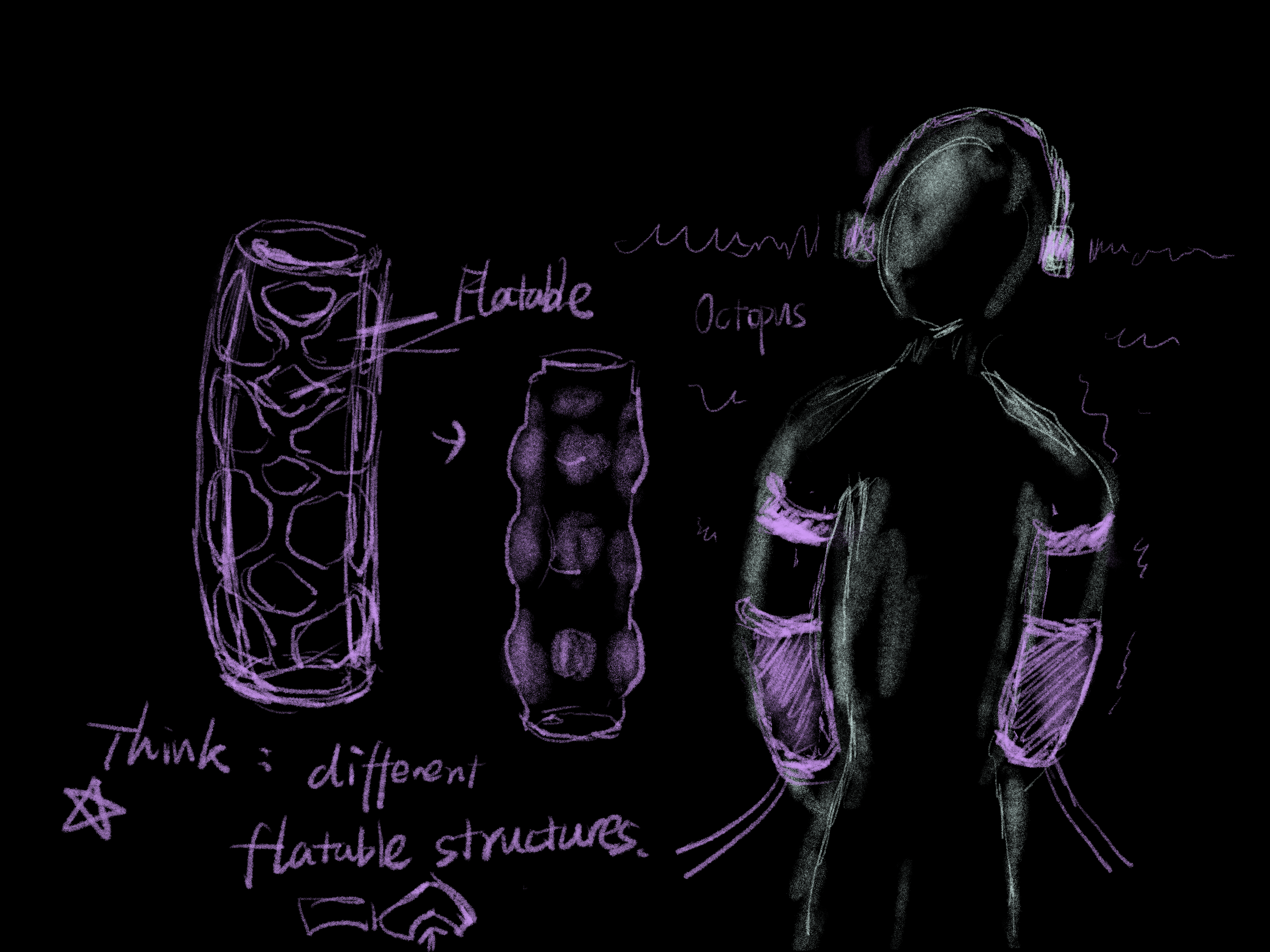
Fabrication: Pneumatic Structures
Inspirations
Materials and Prototype Crafting
“Popping Skin” Prototypes
Sketches
Programmable Texture
Fabrication: Organic-Growth Surface
Interactive Experience
Future Development and Application Scenario
Adaptive and Integrated Wearable Technology
Develop a more sophisticated, AI-powered adaptive system that learns from user interactions to personalize tactile feedback, making the technology wearable and seamlessly integrated into daily life. This would enhance user comfort and engagement across diverse scenarios, from music enjoyment to immersive XR environments.
Expanded Application for Accessibility and Education
Extend the device's utility beyond entertainment to include educational and accessibility tools, particularly for individuals with hearing impairments. Create specialized content libraries that leverage tactile feedback for learning and meditation, making these experiences more inclusive and impactful.
Collaborative and Social Interaction Features
Introduce features that enable users to share and co-create tactile music experiences, fostering a community around tactile music. This could include collaborative platforms for artists and opportunities for users to customize and exchange tactile interpretations of music, broadening the device's appeal and usage.
Music Production
For music producers, the device enriches sound design by allowing creators to feel the music, potentially inspiring new compositions that leverage both auditory and tactile sensations.
Meditation Practice
Meditation practitioners benefit from a more immersive experience as the device translates ambient sounds into tactile feedback, aiding focus and relaxation by engaging an additional sense.
People with Hearing Impairments
It offers people with hearing impairments a novel way to experience music through touch, enabling them to perceive rhythm and melody via tactile feedback, thereby enhancing accessibility and enjoyment of music.
XR Scenarios
In XR environments, the device amplifies immersion by matching virtual audio cues with tactile sensations, adding a layer of realism to VR and AR experiences and making virtual interactions more engaging.